
 |
Exam-Style Questions on GraphProblems on Graph adapted from questions set in previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | GCSE Higher |
Write down the coordinates of the turning point on the graph of \(y = 9 - (x - 5)^2\)
2. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of the curve A with equation \(y=f(x)\) is transformed to give the graph of the curve B with equation \(y=5-f(x)\).
The point on A with coordinates (3, 9) is mapped to the point W on B.
Find the coordinates of W.
3. | GCSE Higher |
Here is a speed-time graph for a drone.
(a) Work out an estimate for the distance the train travelled between the 10th and 15th second.
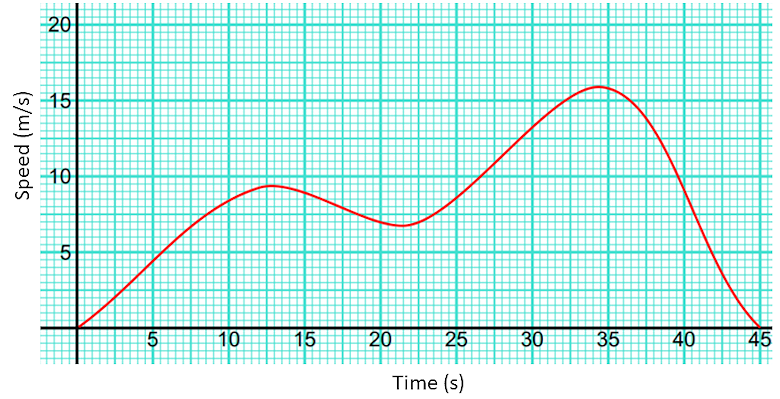
Is your answer to part (a) an underestimate or an overestimate of the actual distance the train travelled during that time? Give a reason for your answer.
Noah used the graph to find out an estimate for the deceleration of the drone at time 35 seconds. He realised that it took ten seconds for the drone's speed to fall to zero.
Here is Noah’s working.
(b) Noah’s method does not give a good estimate of the deceleration at time 35 seconds. Explain why.
4. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of the curve with equation y = \(f(x)\) is shown on the grid below.
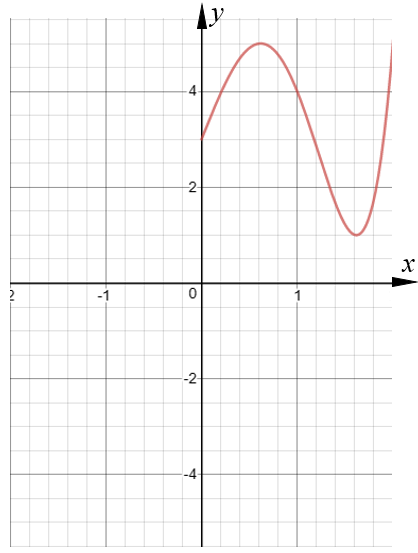
(a) On the grid above, sketch the graph of the curve with equation \(y = f(–x)\)
The red curve with equation \(y = x^2-5x+4\) is transformed by a translation to give the blue curve such that the point (2.5, -2.25) on the red curve is mapped to the point (-2.5, -2.25) on the blue curve.
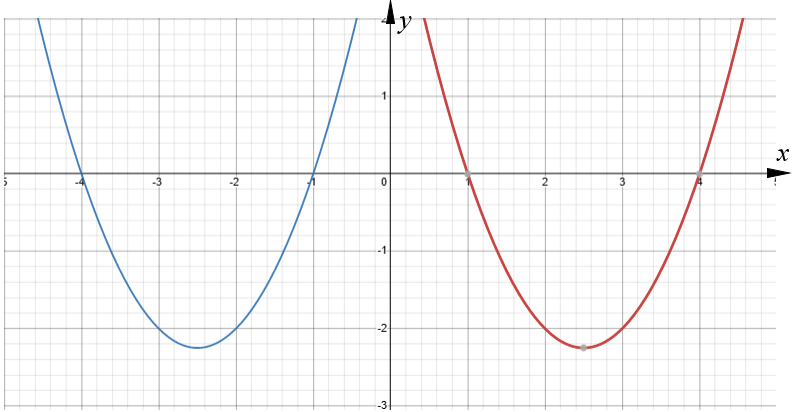
(b) Find an equation for the blue curve.
5. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of the following equation is drawn and then reflected in the x-axis
$$y = 2x^2 - 3x + 2$$(a) What is the equation of the reflected curve?
The original curve is reflected in the y-axis.
(b) What is the equation of this second reflected curve?
6. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Consider the function \(f(x)=\frac{1}{2}\left(2x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)\) for \(x \in \mathbb R\). The following diagram shows part of the graph of \(f\).
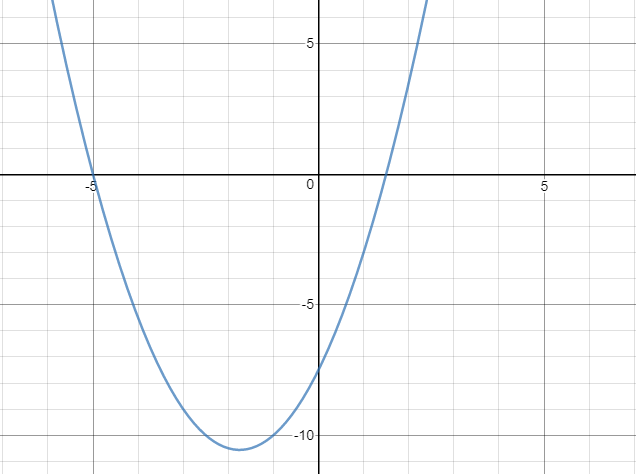
For the graph of \(f\)
(a) find the coordinates of the x-intercepts.
(b) find the coordinates of the vertex.
The function \(f\) can be written in the form \(f(x) = (x+h)^2 + k\)
(c) Write down the value of \(h\) and the value of \(k\).
7. | IB Standard |
A function is defined as \(f(x) = 2{(x - 3)^2} - 5\) .
(a) Show that \(f(x) = 2{x^2} - 12x + 13\).
(b) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry of this graph.
(c) Find the coordinates of the vertex of the graph of \(f(x)\).
(d) Write down the y-intercept.
(e) Make a sketch the graph of \(f(x)\).
Let \(g(x) = {x^2}\). The graph of \(f(x)\) may be obtained from the graph of \(g(x)\) by the two transformations:
(f) Find the values of \(j\), \(k\) and \(s\).
8. | IB Standard |
\(f\) and \(g\) are two functions such that \(g(x)=3f(x+2)+7\).
The graph of \(f\) is mapped to the graph of \(g\) under the following transformations:
A vertical stretch by a factor of \(a\) , followed by a translation \(\begin{pmatrix}b \\c \\ \end{pmatrix}\)
Find the values of
(a) \(a\);
(b) \(b\);
(c) \(c\).
(d) Consider two other functions \(h\) and \(j\). Let \(h(x)=-j(2x)\). The point A(8, 7) on the graph of \(j\) is mapped to the point B on the graph of \(h\). Find the coordinates of B.
9. | A-Level |
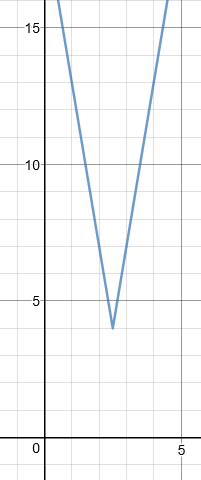
The diagram on the right shows a sketch of part of the graph:
$$ y = f(x) \quad \text{where} \quad f(x) = 3 | 5-2x | + 4 $$
(a) State the range of \(f\).
(b) Solve the equation \(f(x) = \frac{x}{3} + 20 \).
(c) Given that the equation \(f(x) = k\), where \(k\) is a constant, has two distinct roots, state the set of possible values for k.
10. | IB Standard |
Let \(f(x) = {x^2}\) and \(g(x) = 3{(x+2)^2}\) .
The graph of \(g\) can be obtained from the graph of \(f\) using two transformations.
(a) Give a full description of each of the two transformations.
(b) The graph of \(g\) is translated by the vector \( \begin{pmatrix}-4\\5\\ \end{pmatrix}\) to give the graph of \(h\).
The point \(( 2{\text{, }}-1)\) on the graph of \(f\) is translated to the point \(P\) on the graph of \(h\).
Find the coordinates of \(P\).
11. | IB Standard |
(a) Sketch the graph of \(f(x) = 4\sin x - 5\cos x \), for \(–2\pi \le x \le 2\pi \).
(b) Find the amplitude of \(f\).
(c) Find the the period of \(f\).
(d) Find the \(x\)-intercept that lies between 0 and 3.
(e) Hence write \(f(x)\) in the form \(a \sin (bx + c) \).
(f) Write down one value of \(x\) such that \(f'(x) = 0 \).
(g) Write down the two values of \(p\) for which the equation \(f(x) = p\) has exactly two solutions.
12. | IB Standard |
Let \(f(x)=\frac{3x}{x-q}\), where \(x \neq q\).
(a) Write down the equations of the vertical and horizontal asymptotes of the graph of \(f\).
The vertical and horizontal asymptotes to the graph of \(f\) intersect at the point Q(1, 3).
(b) Find the value of q.
(c) The point P(x, y) lies on the graph of \(f\). Show that PQ = \(\sqrt{(x-1)^2+(\frac{3}{x-1})^2}\)
(d) Hence find the coordinates of the points on the graph of \(f\) that are closest to (1, 3).
13. | IB Standard |
Let \(f\) and \(g\) be functions such that \(g(x) = 3f(x - 2) + 7\) .
The graph of \(f\) is mapped to the graph of \(g\) under the following transformations: vertical stretch by a factor of \(k\) , followed by a translation \(\left( \begin{array}{l} p\\ q \end{array} \right)\) .
Write down the value of:
(a) \(k\)
(b) \(p\)
(c) \(q\)
(d) Let \(h(x) = - g(2x)\) . The point A(\(8\), \(7\)) on the graph of \(g\) is mapped to the point \({\rm{A}}'\) on the graph of \(h\) . Find \({\rm{A}}'\)
14. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The graphs of the functions \(f(x)\), a parabola, and \(g(x)\), a straight line, meet at exactly one point.
$$f(x) = px^2 - px $$ $$g(x) = px-5 $$where \( x \in \mathbf R \text{ and } p \in \mathbf R \)
(a) Show that \(p = 5\)
The function \(f\) can be expressed in the form \(f(x) = 5(x-m)(x-n) \text{, where } m,n \in \mathbf R\)
(b) Find the value of \(m\) and the value of \(n\).
The function \(f\) can also be expressed in the form \(f(x) = 5(x-h)^2 + k, \text{ where } h,k \in \mathbf R\)
(c) Find the value of \(h\) and the value of \(k\).
(d) Hence find the values of \(x\) where the graph of \(f\) is both negative and decreasing.
15. | IB Standard |
Two functions are defined as follows: \(f(x) = 2\ln x\) and \(g(x) = \ln \frac{x^2}{3}\).
(a) Express \(g(x)\) in the form \(f(x) - \ln a\) , where \(a \in {{\mathbb{Z}}^ + }\) .
(b) The graph of \(g(x)\) is a transformation of the graph of \(f(x)\) . Give a full geometric description of this transformation.
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.
Do you have any comments about these exam-style questions? It is always useful to receive feedback and helps make this free resource even more useful for those learning Mathematics anywhere in the world. Click here to enter your comments.